As GPT model usage grows in companies, two problems emerge: maintaining oversight and keeping costs under control—without creating security risks. This is where the OpenAI Admin CLI from ADMIN INTELLIGENCE comes in: a lean command‑line solution to centrally manage and automate organization, projects, users, service accounts, API keys, rate limits, and usage and cost data. This post is part 2 of our OpenAI API security series. Part 1: OpenAI Key Rotation: A Practical Guide to Secure API Keys Without Downtime focuses on safe key rotation in production environments.
Context note: OpenAI recently introduced an Admin API for organization‑wide management (vendor statements point to a launch at the end of October 2025; check your organization’s current OpenAI documentation). The CLI shown here uses exactly these interfaces so admins can execute administrative tasks reproducibly, scriptably, and safely—up to full automation.
What the OpenAI Admin CLI does
The OpenAI Admin CLI structures typical admin tasks across clear subcommands. You get:
- Visibility into all users and projects of an organization
- Service accounts with automatically generated API keys for CI/CD and automation
- API key management (including detailed queries and deletion of user keys)
- Rate‑limit control per model/project for cost governance
- Usage analytics (completions, embeddings, images, audio TTS/transcription)
- Cost tracking with grouping by projects and line items
- Output as table or JSON—ideal for pipes, scripting, and dashboards
The goal: governance, security, and cost control become configurable and automatable—instead of manual and error‑prone.
You can find the CLI repository here.
Security model and organizational guardrails
OpenAI’s Admin API works with admin keys (organization level). This leads to a few principles:
- Least privilege: The admin key belongs only in secured admin contexts. Never in app code, regular CI jobs, or end‑user scripts.
- Ownership and roles: Only organization owners can create admin keys. Manage their lifecycle and documentation clearly.
- Secrets storage: Use a dedicated secrets manager or a secure password manager. For teams aiming for a professional setup, our comparison “Vaultwarden vs Passbolt – der große Passwortmanager‑Vergleich für Admins und Teams” is worth a look.
- Service accounts instead of personal keys in production: This prevents access breaks when employees leave.
Identity governance and SSO also help manage user access cleanly. For a thorough look at modern IdP solutions, see our “Identity Provider Vergleich – Authentik vs Keycloak”.
Installation and basic configuration
Requirements: Python 3 and Pip.
# Fetch repository locally (clone or download)
# Install dependencies
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
# Set admin key as environment variable
export OPENAI_ADMIN_KEY="sk-admin-..."You can also pass the key per invocation:
python openai_admin.py --admin-key sk-admin-... users listOptionally make the script executable:
chmod +x openai_admin.pyDefault output is a readable table. For automation, use JSON plus jq:
python openai_admin.py users list --format json \
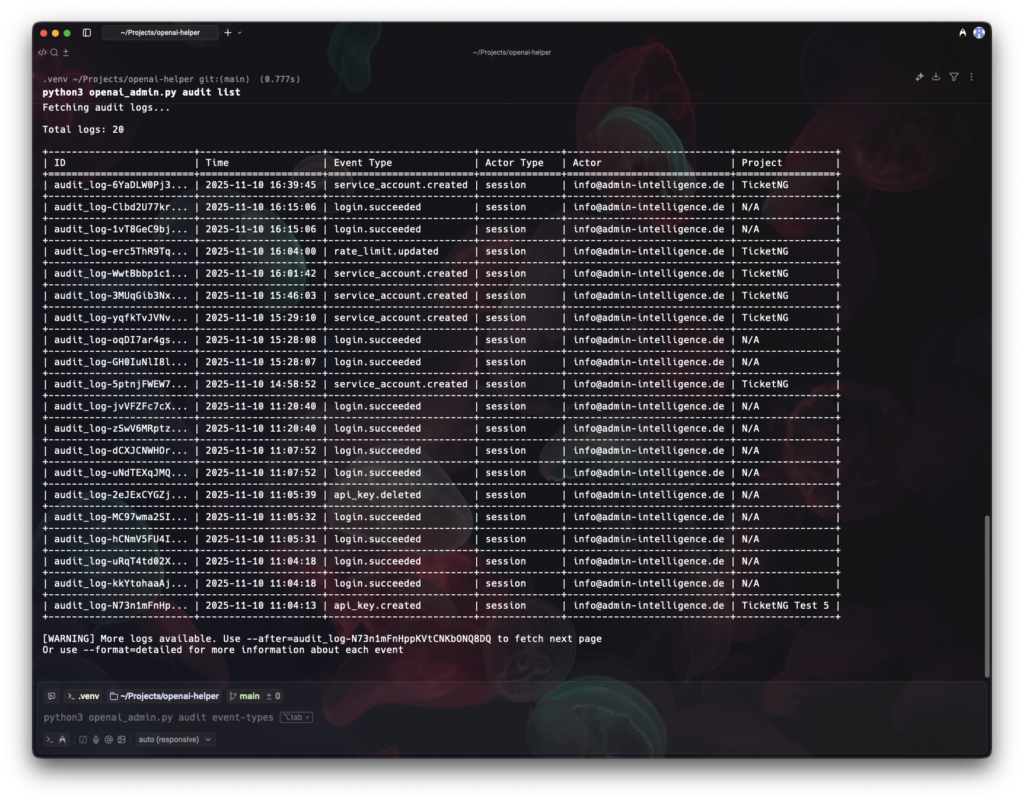
| jq '.data[] | {name, email, role}'Audits: Users and projects at a glance
Transparency is the first step toward security and cost control.
- List organization‑level users:
python openai_admin.py users list
# JSON for downstream analysis
python openai_admin.py users list --format json- View projects (including archive):
python openai_admin.py projects list
python openai_admin.py projects list --include-archivedPractical benefits:
- Role audit: Who is owner, who is member?
- Project hygiene: Spot and clean up archived projects
- Prepare for key and budget governance
Service accounts: Stability for production and CI/CD
Service accounts are bot identities without personal linkage—ideal for production apps, pipelines, and automation. Benefit: offboarding individuals does not interrupt production.
List service accounts of a project:
python openai_admin.py service-accounts list proj_abc123
python openai_admin.py service-accounts list proj_abc123 --format jsonCreate with auto‑generated API key:
python openai_admin.py service-accounts create proj_abc123 "Production Bot"Important: The generated key is shown only once. Store it immediately in your secrets manager. If it is lost, you must delete the service account and create a new one.
Retrieve details and delete:
python openai_admin.py service-accounts get proj_abc123 svc_acct_xyz
python openai_admin.py service-accounts delete proj_abc123 svc_acct_xyz --forceProven pattern for rotation in production:
- Create a new service account with a new key
- Switch deployments/secrets and verify
- Remove the old service account (including key invalidation)
For CI/CD integration, we recommend our hands‑on guide “GitLab CI/CD für Administratoren – ein Praxis‑Guide für automatisierte Deployments”. It shows how to handle secrets safely in pipelines.
Manage API keys—separately for users and service accounts
The Admin CLI deliberately distinguishes:
- User keys: Can be deleted individually
- Service account keys: Not individually deletable; delete the entire service account instead
List admin keys:
python openai_admin.py keys list-adminShow project keys (users and service accounts):
python openai_admin.py keys list-project proj_abc123Key details:
python openai_admin.py keys get proj_abc123 key_xyz789
# JSON for scripting
python openai_admin.py keys get proj_abc123 key_xyz789 --format jsonDelete user keys:
python openai_admin.py keys delete proj_abc123 key_xyz789
# without prompt
python openai_admin.py keys delete proj_abc123 key_xyz789 --forcePractical advice—key rotation without downtime: Organize deployments so new keys are introduced and old keys are revoked only after verified go‑live. We described detailed patterns, pitfalls, and rollback options in part 1 of the series (see title above).
Rate limits as guardrails for cost and abuse protection
With rate limits, you set clear per‑project and per‑model caps—for requests, tokens, images, and audio. This avoids outliers and protects budgets.
View a project’s configuration:
python openai_admin.py rate-limits list proj_abc123
# JSON for further processing
python openai_admin.py rate-limits list proj_abc123 --format jsonKey fields in the output:
- Model name (e.g., gpt‑4, gpt‑4o, dall‑e‑3)
- max_requests_per_minute, max_tokens_per_minute
- max_images_per_minute, max_audio_mb_per_minute
- max_requests_per_day, batch_max_tokens_per_day
The Admin API does not provide a single‑item query per rate limit; use the list view and filter via script.
Change limits:
# Throttle GPT‑4 usage
python openai_admin.py rate-limits update proj_abc123 rl_gpt4 \
--max-requests-per-minute 50 \
--max-tokens-per-minute 10000
# DALL‑E with a daily budget
python openai_admin.py rate-limits update proj_abc123 rl_dalle3 \
--max-images-per-minute 5 \
--max-requests-per-day 100
# Scale up production
python openai_admin.py rate-limits update proj_prod rl_gpt35turbo \
--max-requests-per-minute 5000 \
--max-tokens-per-minute 1000000Rules:
- Limits cannot exceed organization‑level limits
- Keep dev/test conservative, scale production as needed
- Validate limits regularly against real usage
Proven profiles:
- Development/test (cost brake):
python openai_admin.py rate-limits update proj_dev rl_gpt4 \
--max-requests-per-minute 10 \
--max-tokens-per-minute 5000- Production (business‑critical):
python openai_admin.py rate-limits update proj_prod rl_gpt4 \
--max-requests-per-minute 1000 \
--max-tokens-per-minute 500000- Daily cost cap:
python openai_admin.py rate-limits update proj_abc123 rl_gpt4 \
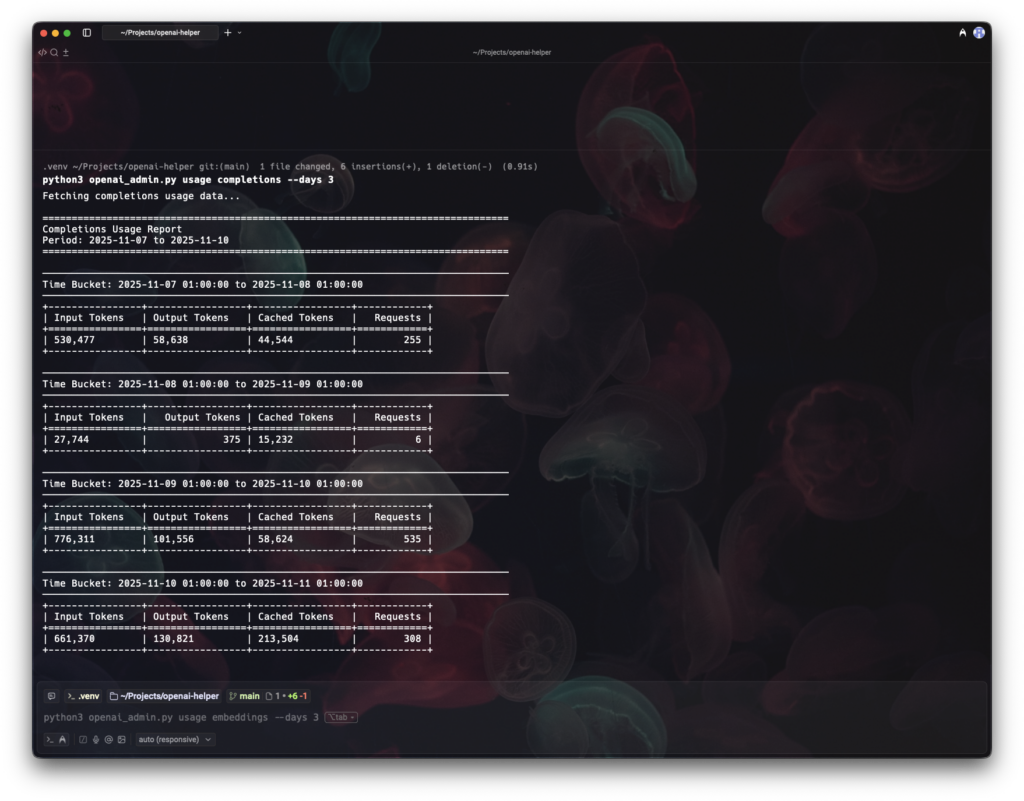
--max-requests-per-day 10000Analyze usage: Completions, embeddings, images, and audio
The usage commands return time series, grouped by project, user, key, model, etc. This supports anomaly detection, capacity planning, and chargeback.
Completions (chat/text):
# last 7 days
python openai_admin.py usage completions --days 7
# exact period
python openai_admin.py usage completions --start-date 2024-01-01 --end-date 2024-01-31
# group by project and model
python openai_admin.py usage completions --days 30 \
--group-by project_id --group-by modelEmbeddings:
python openai_admin.py usage embeddings --days 7Images (e.g., DALL‑E):
python openai_admin.py usage images --days 7Audio TTS/transcription:
python openai_admin.py usage audio-speeches --days 7
python openai_admin.py usage audio-transcriptions --days 7Tips:
- Combine groupings (e.g., project_id and model) to spot hotspots.
- Use JSON output for dashboards or data frames.
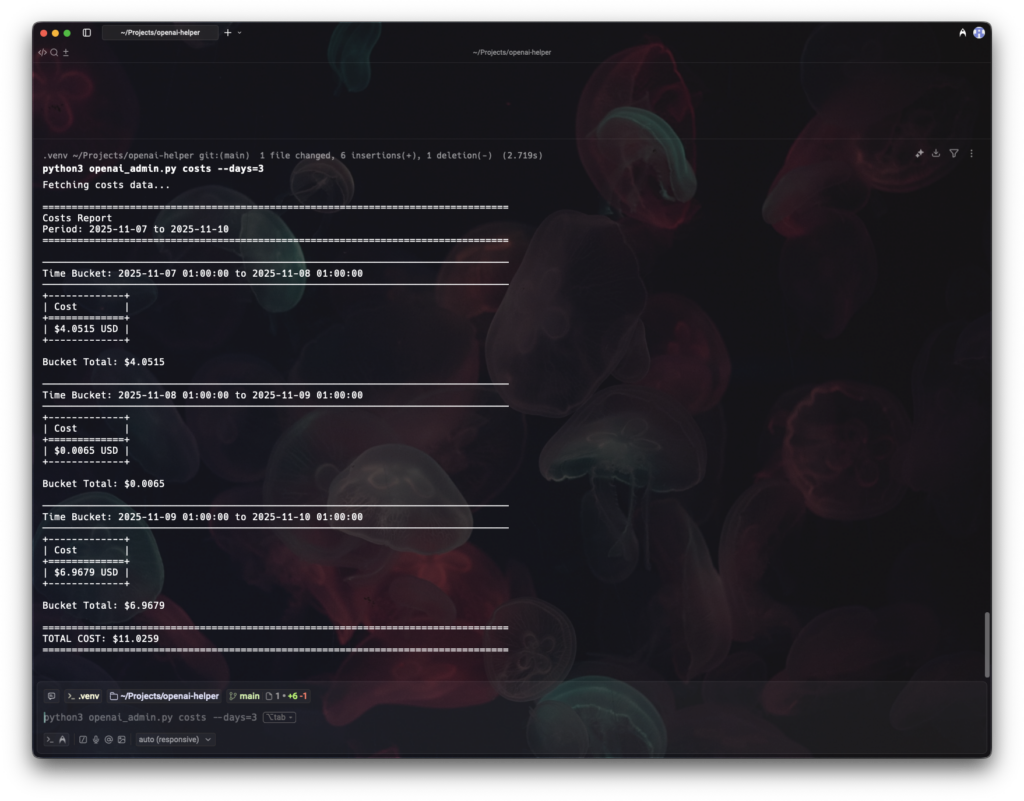
Stay on top of costs: analysis and budgets
Cost transparency is essential—well before month‑end. The CLI offers time series, groupings, and filters.
Examples:
# costs of the last 30 days
python openai_admin.py costs --days 30
# group by project
python openai_admin.py costs --days 30 --group-by project_id
# by line item (fine breakdown)
python openai_admin.py costs --days 7 --group-by line_item
# filter a specific project
python openai_admin.py costs --days 30 --project-id proj_123CSV export via jq (ad‑hoc):
python openai_admin.py costs --days 30 --format json \
| jq -r '.buckets[] | [.start, .end, (.amount|tostring), .currency] | @csv' \
> costs_last30d.csvBest practices:
- Define budgets per project and safeguard them with rate limits
- Automate regular cost reports
- Correlate peaks: identify cost‑intensive models/projects
Automation: From one‑off action to repeatable governance
The Admin CLI shows its strength in pipelines and scheduled jobs. A realistic set:
- Nightly audit job (users, projects, keys), store JSON as artifacts, and run differential checks
- Generate weekly cost reports and distribute to FinOps/teams
- Set rate limits based on policy (per project and environment)
- Orchestrate key rotation in CI: create a new service account, update secret, run smoke tests, remove old account
A minimal example for GitLab CI (greatly simplified):
stages: [audit]
variables:
PYTHONUNBUFFERED: "1"
openai_audit:
stage: audit
image: python:3.12-slim
rules:
- if: "$SCHEDULED_PIPELINE == 'true'"
script:
- pip install -r requirements.txt jq
- python openai_admin.py users list --format json > users.json
- python openai_admin.py projects list --format json > projects.json
- python openai_admin.py costs --days 7 --format json > costs.json
- jq '.buckets | length' costs.json
artifacts:
when: always
paths: [users.json, projects.json, costs.json]
expire_in: 7 daysHow to embed and mask secrets safely in GitLab is explained in detail in “GitLab CI/CD für Administratoren – ein Praxis‑Guide für automatisierte Deployments”.
For security monitoring, a central SIEM is also worthwhile. Our post “Wazuh SIEM – Open‑Source Sicherheit auf den Punkt gebracht” shows how to consolidate events—ideal for observing API usage anomalies, failed calls, or unusual cost peaks.
Governance practices: structure, naming, separation
Technology alone is not enough. Establish rules:
- Exactly one business purpose per project: Separate production apps, back‑office automations, experiments, batch jobs.
- Environment separation: proj_appX_dev, proj_appX_stage, proj_appX_prod—with different limits and budgets.
- Consistent naming: Clear names for service accounts (“GitHub Actions”, “Prod API Bot”), documented in the team knowledge base.
- Make rotation a habit: Recurring jobs, defined escalation paths, emergency playbooks.
- Version reports: Store JSON snapshots of usage and cost data in a secure repository; review changes.
Operations, troubleshooting, and hardening
Typical pitfalls and quick fixes:
- Missing environment variable:
export OPENAI_ADMIN_KEY="sk-admin-..."- Import errors: update dependencies
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt- API errors: check validity of the admin key, ensure owner role, verify expiry/rotation if applicable
Hardening recommendations:
- Never leak the admin key into VCS, logs, or artifacts; enable secrets scanning
- Use service accounts instead of personal keys in all automated paths
- Combine budgets, limits, and usage alerts (costs, requests, tokens)
Limits and roadmap
The current Admin API feature set covers core needs. Note:
- Rate limits are returned only as a complete list per project; single‑item retrieval is not provided
- Service account keys cannot be deleted individually—rotate by creating new service accounts
- Future extensions are planned (e.g., audit‑log queries, CSV/Excel exports, budget alerts)—keep your tooling roadmap flexible
If you apply the patterns shown in this post to your organization, you gain clear visibility into users, projects, costs, and risks—and you can practice governance as code. You can always find more in‑depth, hands‑on articles on our blog at https://blog.admin-intelligence.de/. For tailor‑made LLM architectures, security concepts, and automation, we also support you on a project basis—learn more on our AI & LLM services page: AI & LLM Consulting von ADMIN INTELLIGENCE. If you have questions about implementation, integration with GitLab, or hardening your admin processes, reach out directly via Contact.

Project Manager, Lead Dev
